Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) and Wireless Signal Strength
For best performance in a wireless environment, it is key that wireless devices are able to distinguish received signals as legitimate information they should be listening to and ignore any background signals on the spectrum.
For best performance in a wireless environment, it is key that wireless devices are able to distinguish received signals as legitimate information they should be listening to and ignore any background signals on the spectrum. There is a concept known as the Signal to Noise Ratio or SNR, that ensures the best wireless functionality. The SNR is the difference between the received wireless signal and the noise floor. The noise floor is simply erroneous background transmissions that are emitted from either other devices that are too far away for the signal to be intelligible, or by devices that are inadvertently creating interference on the same frequency.
For example, if a client device's radio receives a signal at -75 dBm, and the noise floor is -90 dBm, then the effective SNR is 15 dB. This would then reflect as a signal strength of 15 dB for this wireless connection.
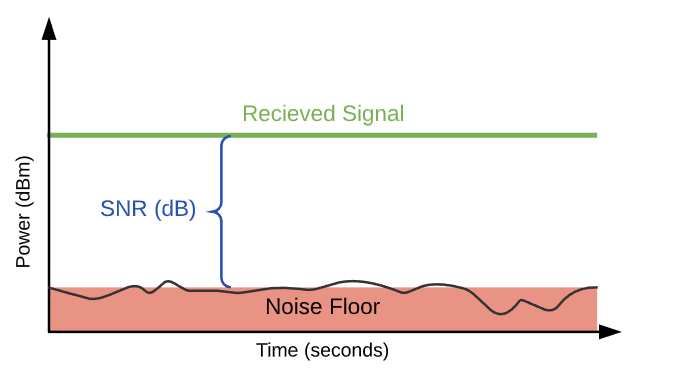
The further a received signal is from the noise floor, the better the signal quality. Signals close to the noise floor can be subject to data corruption, which will result in retransmissions between the transmitter and receiver. This will degrade wireless throughput and latency as the retransmitted signals will take up airtime in the wireless environment.
Access Points reference the Signal to Noise Ratio as the indication for the quality of the wireless connection. This provides a more accurate depiction of the health of the wireless signals as it takes the RF environment and ambient noise levels into account. For instance, a received signal of -65 dBm can be considered good at a location that has a noise floor of -90 dBm (SNR 25 dB) but not so much at a location with a noise floor of -80 dBm (SNR 15 dB).
Generally, a signal with an SNR value of 20 dB or more is recommended for data networks where as an SNR value of 25 dB or more is recommended for networks that use voice applications. [Source]