WiFi Scanner for Mac OS User Guide
Introduction
WiFi Scanner is an 802.11/WiFi wireless scanner and connection manager for 802.11 a/b/g/n/ac networks. WiFi Scanner is an easy to use tool for designing, verifying, and troubleshooting WiFi coverage. The tool provides information such as signal strength, noise, manufacturer name based on MAC address prefix of device (OUI), and AP channel assignments for WiFi access points.
WiFi Scanner can also be used a security tool for detecting unauthorized and rogue access points. The app includes an audio alert (beep) feature that is directly related to RSSI / access point signal strength. This feature can be used to track down devices by listening for beep frequency instead of watching the app screen.
The Speed Tester is a feature to WiFi Scanner which tests the ping, download and upload speeds to one three closest Internet Speed Test Servers.
A Network IP Scanner has been added to WiFi Scanner feature set. Users can utilize this tool to view who and what is currently on their network.
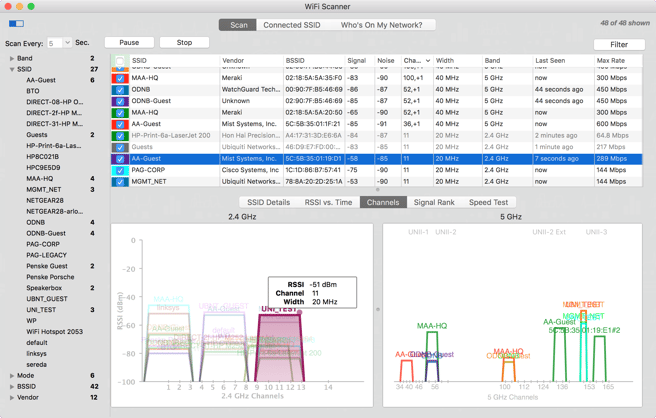
"Scan" Tab
The Scan tab allows the user to scan for networks using the computer’s built-in capabilities. Users can filter results, gain more information about each network, view network congestion, as well as test speeds on the network the user is connected.

Controls and Filters
The default setting is 5 seconds for every scan, which means that WiFi Scanner will run tests every 5 seconds until the user pauses or stops the scan. This ensures that the user has refreshed data as quickly as possible.
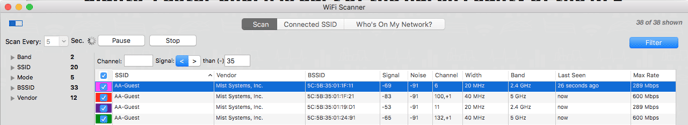
The filters are very helpful when the user is trying to narrow down the results in a high-volume area. These features can be utilized before, during, or after the current scan has been performed.
The left side filter is accessed by the tab icon in the upper left-hand corner. Users can select an option and it will be filter on the right-hand table. Use SHIFT and COMMAND keys to select multiple values. It is categorized by:
- Band (2.4 GHz or 5 GHz)
- SSID
- Mode (802.11b/g/n/ac)
- BSSID
- Vendor (this can be updated via Help menu and choosing Update Vendor OUI and)
The FILTER button on the right-hand side opens up a secondary filter. Simply enter the Channel (add multiple by separating by commas) / Signal fields and hit enter on the keyboard to activate those filters.
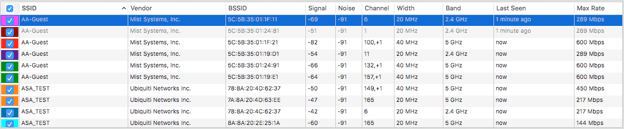
Information Chart
The information gathered is separated into columns. These columns can all be rearranged except for the Check Boxes, and SSID. The network that the user is connected to will be highlighted in this section with a yellow hue. Columns can be toggled on/off from the preferences menu.
General Column Definitions
| Ad-Hoc | Whether the network is setup as and Ad-Hoc or not |
| BSSID / MAC Address | The MAC address or unique address that identifies each specific device |
| CC | The Country Code of a network (if given by the Access Point) |
| Channel | The specific channel a network is operating on |
| Channel Band | The frequency range that a network is operating on |
| Channel Width | The size of the channel |
| Check Boxes | When networks are checked, they will display in the various graphs |
| Join |
Allows the user to connect to a specific network* *Note: Specific APs may force the users device to the best RSSI, so users will Join an AP, only to be immediately moved to the ones the APs choose. |
| Last Seen | A time stamp for when the last time a device was detected |
| Max Rate | The maximum speed an Access Point can send and receive data |
| Noise | The amount of interference that is in a signal |
| PHY Mode | The type of protocol a network’s Access Point is using |
| S/N | Signal to Noise Ratio (The higher the positive number, the better) |
| Security | The type of security that a device currently has implemented |
| Signal | The signal strength or RSSI received from a device |
| SSID | The name of a network. If the user has multiple Access Points on one network, then there could be multiple SSIDs with the same name (but will have varying BSSIDs) |
| Streams | The number of spatial streams an Access Point is capable of transmitting and receiving |
| Tag | Double Click this column to add a “tag” of your choice to the selection and further organize the chart |
| Vendor OUI | The manufacturer of the Access Point |
| WPS | Whether WiFi Protected Setup is enabled or not |
Advanced Column Definitions
Note: Not all advanced information can be collected from every Access Point.
| 802.11r | Currently supported by iOS & OSX, this 802.11 standard is an essential part of the WiFi Alliance "Voice Enterprise" certification and permits Fast Secure Roaming in less than 20 milliseconds |
| # Client | Quickly determine the amount of clients connected to an AP (If QBSS Load enabled in the infrastructure). Great for analyzing client distribution in a high-density environment with multiple AP's |
| AP Name | Identify signal strength to AP's by name. No need to correlate which BSSID MAC address belongs to which AP |
| Channel Utilization | A snapshot of the AP's perspective on Channel Utilization. Great for spotting a potential problem, you may want to investigate |
| Protection Mechanisms | Quickly determine whether you have legacy devices in or around your 802.11n network that are slowing network down to do protection mechanisms getting enabled |
Speed Test Column Definitions
| Avg Down Speed | Average download speed of all tests run on an Access Point |
| Avg Up Speed | Average upload speed of all tests run on an Access Point |
| Max Down Speed | Maximum download speed of all tests run on an Access Point |
| Max Up Speed | Maximum upload speed of all tests run on an Access Point |
| Min Down Speed | Minimum download speed of all tests run on an Access Point |
| Min Up Speed | Minimum upload speed of all tests run on an Access Point |
| Recent Down Speed | Most recent download speed run on an Access Point |
| Recent Up Speed | Most recent upload speed run on an Access Point |
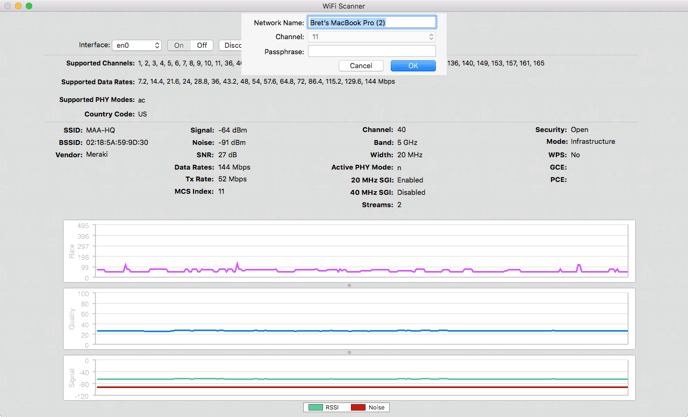
Selected Network Information: SSID Details
Clicking on a row in the information chart highlights the row in blue and displays that network’s information in the SSID Details section. This is where most of the information gathered about a network is displayed.
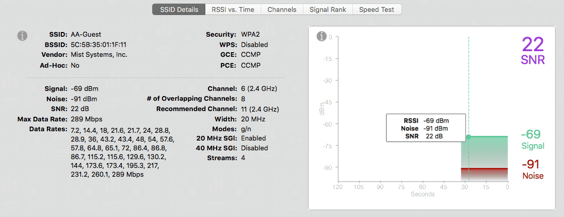
New Features
# of Overlapping Channels - Shows the complete number of channels that may be interfering with the selected network.
Recommended Channel - Suggests the best channel for the selected network with the least amount of possible interference, based on overlap and usage.
Troubleshooting Graphs
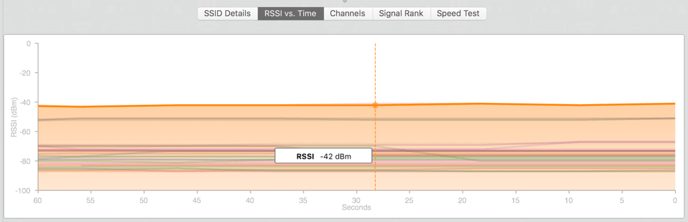
RSSI vs. Time
The networks that are checked in the Information Chart will be graphed in these graphs. The RSSI vs. Time graph, which displays the signal strength or RSSI (received signal strength indicator) over time. Selecting a specific network that is checked will highlight that network in the graphs, as well as dim the others.
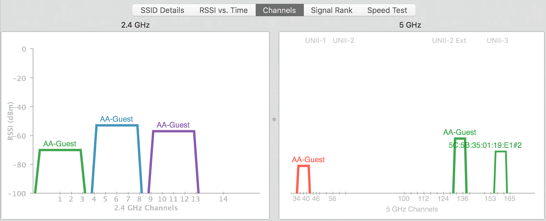
Channels
The Channels graph displays all the networks that are checked in the Information Chart. The recommended channels for 2.4 GHz Band are 1, 6, and 11 because they allow for the best spread of frequency without overlap (interference) with other networks. Choosing the most vacant of the recommended channels for the user’s network will ensure the best chance for the strongest signal with the least amount of noise.
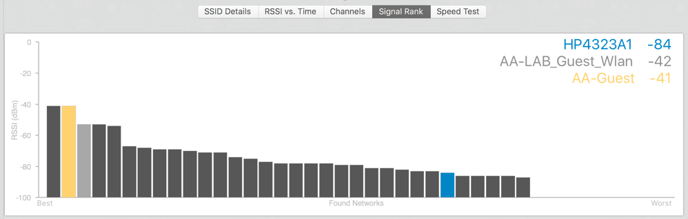
Signal Rank
Signal Rank is a feature that plots all of the checked networks signal strength, for a quick and easy comparison. This graph will also highlight other Access Points on the same network, which allows users to see which Access Point might give them the best and/or fastest connection.
Blue indicates which Access Point is selected in the Information Chart.
Yellow indicates the Access Point a user is currently connected to.
Users can select a bar to view which network it belongs too, which is indicated by the grey color.
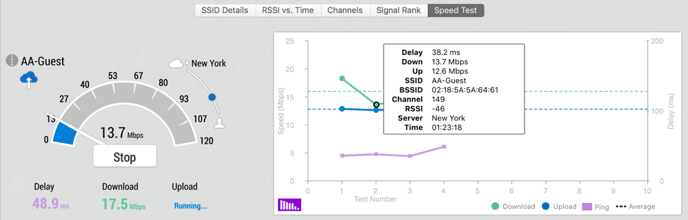
Speed Test
From this tab, the user can test download and upload speed, as well as the connection delay. Users can choose from various servers to test to around the world. The results are graphed and recorded within the app, which can be accessed by clicking the i button to the left. Clicking the purple bar graph icon changes the plot graph to a bar graph that ranks the test results based on download or upload speed.
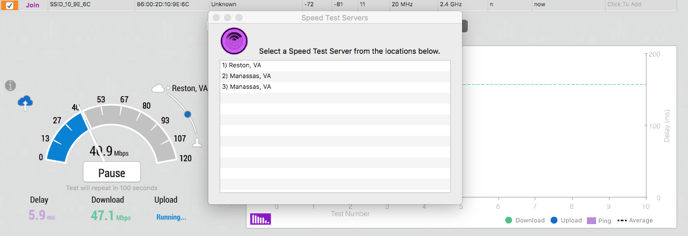
Speed Test: Change Servers
By default, WiFi Scanner will try to connect to the fastest server available to the user. Users manually select a server by clicking on the server name (see image below.) This will provide a pop up window with a list of closest servers to test to.
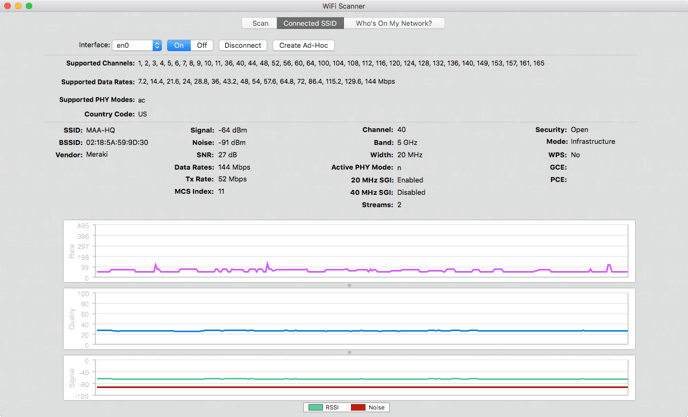
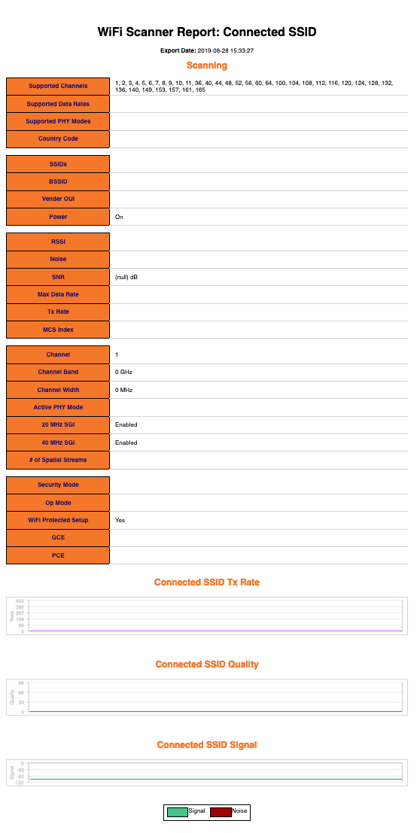
“Connected SSID” Tab
The tab entitled Connected SSID contains information describing the static and dynamic state of the currently connected wireless network. Additionally, it allows the user to toggle interface power (ex: turn off WiFi Radio), disconnect from the current network, and create and Ad-Hoc network through the current machine.
The app supports a multiple interface scenario, whereby the machine could have several IEEE 802.11 wireless interfaces. The popup button on the top left corner of the app allows the user to select which interface should be set as the current interface. By default, the popup button will select the primary WLAN interface for the system.
Create Ad-Hoc
This forms an Ad-hoc network that allows other devices to connect to the user’s device directly. Power option must be in the ON position in order to create an IBSS.
"Who's On My Network" Tab
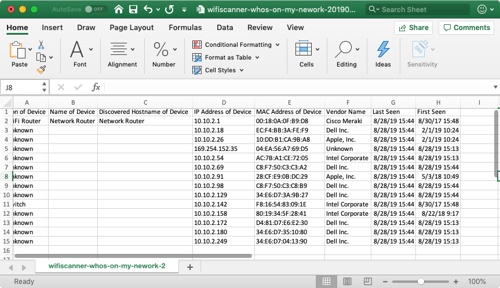
WiFi Scanner’s newest feature is a Network IP Scanner that looks for devices that are currently connected to the user’s network. This helps troubleshooting speed and connection problems users may be experiencing by giving them a list of connected devices (the more devices, the more network usage might be happening).
Results
All of the devices currently connected to the network should appear in the results list. WiFi Scanner will collect as much data as possible about the device, such as its name, IP Address, manufacturer, etc. If WiFi Scanner cannot identify the type of device or its name, the user can assign a name and icon for that device, which is saved for future scans.
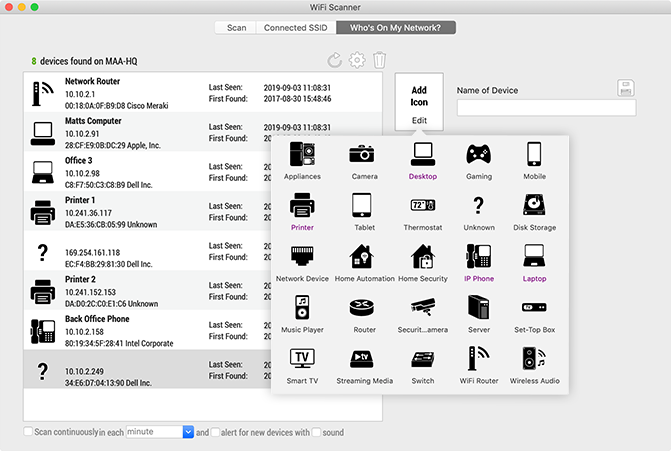
Information gathered about the devices is as followed:
IP Address
This number is an address all information technology devices (printers, routers, modems, ect.) use which identifies and allows them the ability to communicate with each other on a computer network. Each device is assigned an IP Address when it connects to a network.
Hostname
The name, if assigned, that the owner of the device chooses.
MAC Address
A Media Access Control Address, also known as a hardware or physical address, is a unique value associated with the network adapter on any network-connected device. These are unique to each and every device.
Vendor
The manufacturer of the device.
Last Seen
The last time the device was seen on the network by WiFi Scanner.
First Found
The first time the device was seen on the network by WiFi Scanner.
Preferences Menu
The Preferences Menu gives access to additional features, including showing or hiding specific columns in the information chart, changing graph views, and customizing speed test settings.
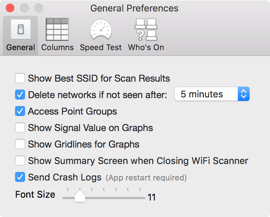
General Preferences
Show Best SSID for Scan Results - This allows devices that are on the same network (such as multiple routers or access points) to be combined into one result, displaying the one with the best signal.
Delete networks if not seen after – Clears old scanned information
Access Point Groups – Combines results that are from the same Access Point on the Graphs
Show Signal Value on Graph - Automatically add the signal values (RSSI values) to the time spots on the graphs for each network shown on the graph for “RSSI vs. Time”.
Show Gridlines for Graphs - Add gridlines to the x-axis and y-axis for all graphs.
Show Summary Screen when Closing WiFi Scanner - Turn on/off the pop-up summary screen seen when the app is closed.
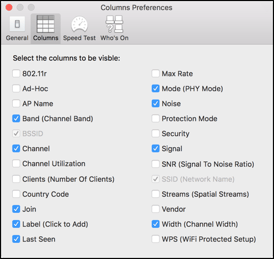
Columns Preferences
Simply right-clicking the column titles and checking/unchecking can hide the columns. The user can also toggle which ones are in view under the Preferences Menu.
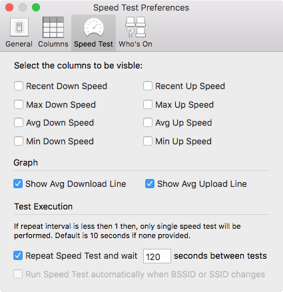
Speed Test Preferences
Show Avg Download Line / Show Avg Upload Line - Turn the dotted averages lines on/off for the Speed Test graph.
Repeat Speed Test - Allows the user to have continuous speed tests running with a wait time between entire test sets.
Run Speed Test automatically - allows the user to have speed tests running as they move across a network, such as one with multiple Access Points or varying networks.
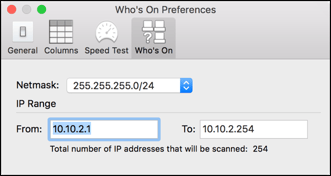
Who's On Preferences
Preferences for the Who’s On My Network? tab include an IP Address range. By default it will choose the current subnet you are connected to and search all the IPs within that range X.X.X.1 – X.X.X.254. The default Netmask (255.255.255.0/24) is what most home networks use. It can be changed to shrink or enlarge the IP Range that will be scanned.
Other Features
Audio Tracking
Double Clicking on one of the networks will pop up a window that shows specific test results for a selected network, at particular intervals. This window also has a device location feature called Audio Tracking. When turned on, an audible beep will emit from the user’s machine in relation to the signal strength of a network device (router or access point). While moving the user’s machine (such as a laptop) around, the beep will become faster or slower depending on the strength of the signal. The faster the beep, the closer the machine is to the actual network device.
This feature is used to find rogue agents that might be hidden, for example, in walls or ceilings.
![]()
Exports and Reports
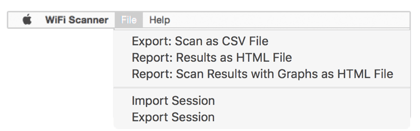
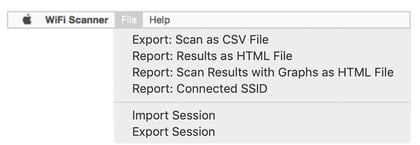
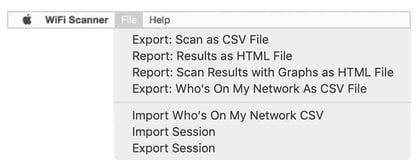
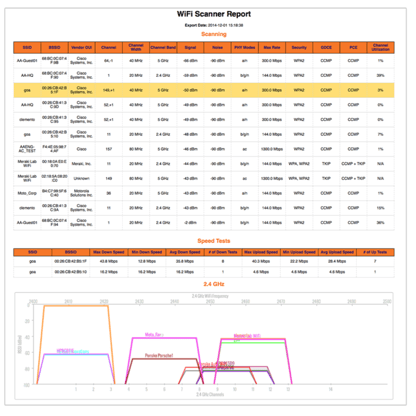
Exporting the scan results allows the user to send this information to administrators that need this information for troubleshooting network problems. Exports and reports come in CSV, HTML, and HTML with graphs formats.
Users can also Import / Export scan sessions / CSVs and use across platforms (Mac/Windows).
Scan Tab Preferences:
Connected SSID Tab Preferences:
Who's On My Network? Tab Preferences:
Export Scan Results with Graphs as HTML Example:
Export Connected SSID Example:
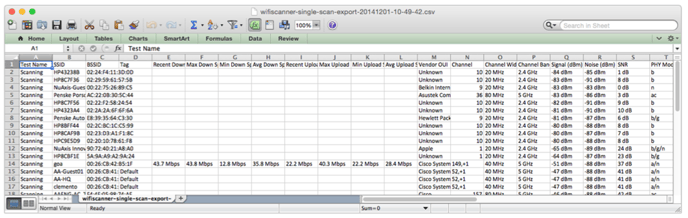
Exported Scan Results CSV Example:
Exported Who's On My Network Results CSV Example: